Vault
Adaptive overload protection
Enterprise
Appropriate Vault Enterprise license required
Beta feature
Beta functionality is stable but possibly incomplete and subject to change. We strongly discourage using beta features in production deployments of Vault
Adaptive overload protection refers to a set of features in Vault Enterprise that prevent client requests from overwhelming different server resources leading to poor availability.
Preventing overload
Vault currently supports one type of adaptive overload protection that prevents Vault servers from being overwhelmed by write requests.
These protection measures are "Adaptive" in the sense that they automatically and continuously adjust to maintain optimal performance for the current workload and hardware resources available without any user tuning.
Load testing and tuning of appropriate limits is time consuming for users during initial setup. Even when clusters are carefully tuned during installation, real-world workloads and hardware performance both change over time. A static tuning will soon be sub-optimal or even completely ineffective at preventing overloads.
For example, an increase in disk latency caused by failing hardware might reduce the server's available throughput. A static limit configured while disks were performing a their peak would not protect the degraded system from overload. By adaptively responding to current load and performance characteristics, Vault Enterprise is able to provide long-term protection against overloads.
Types of overload
There are many potential resources that could become a performance bottleneck in a Vault Enterprise cluster. Different forms of adaptive overload protection target specific components and workloads. This allows each one to be carefully specialized and tuned to the needs of that sub-system. The sections below describe specific mechanisms that prevent overload of particular subsystems and protect against particular types of overloads.
Write overload protection
In Vault Enterprise, all writes go through the WALBackend to allow for
replication to other clusters. This is true even if replication is not being
used. Vault performs batching or "group commit" for these writes to increases
throughput. Optimal throughput for a given storage backend is obtained when
there are enough write requests in the queue to fill the next batch. However, if
there are more requests queued than will fit in a batch, latencies start to grow
quickly as all writes have to wait behind multiple other batches.
In some cases, a sudden influx of write requests that exceeds Vault's hardware capacity can result in the writes queueing for so long that every request times out before the write can make it through the queue. This makes Vault effectively unavailable to clients even though it is still processing requests and storing data as fast as it can. This is illustrated in the test results shown below for a workload of 100% logins.
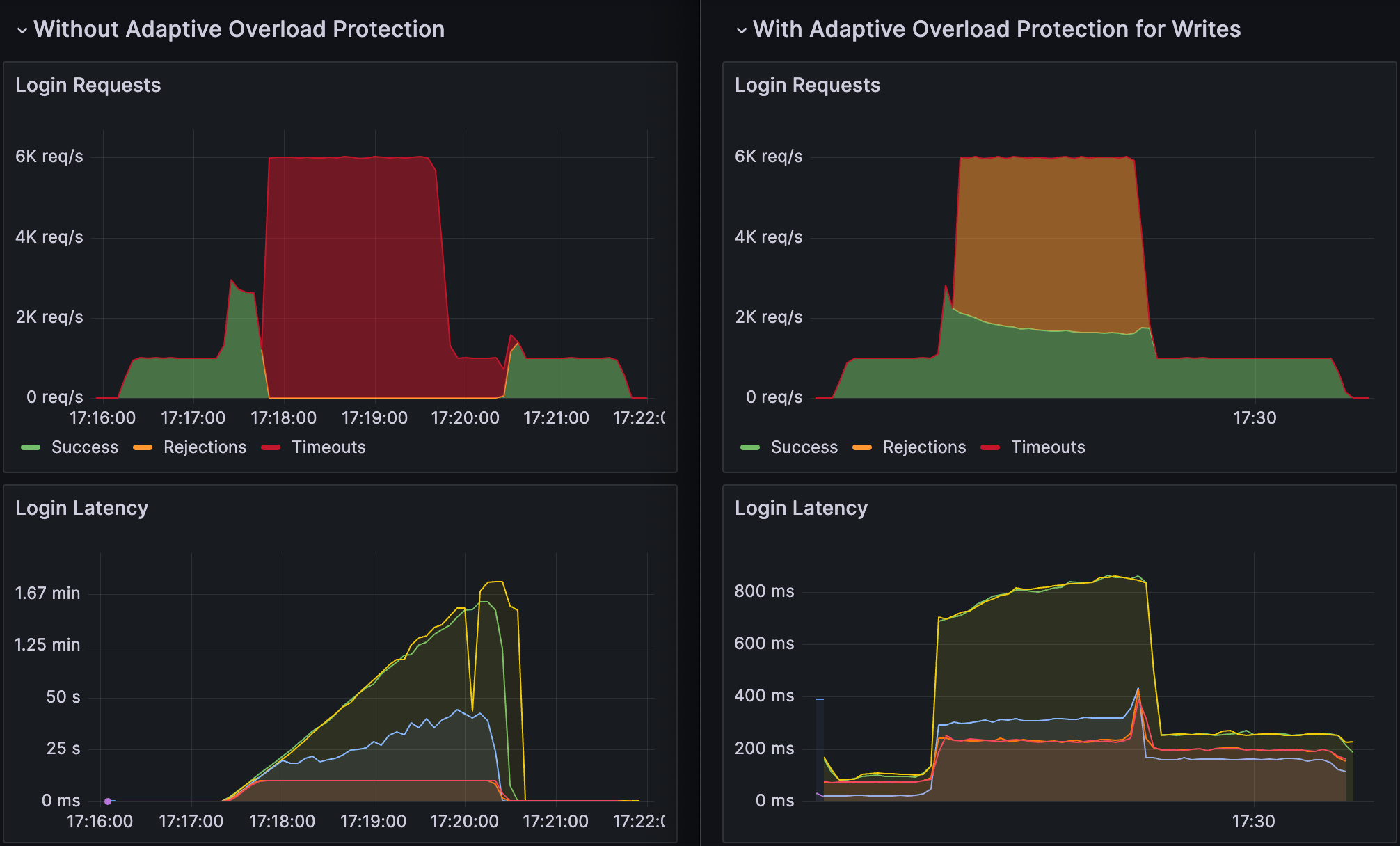
Adaptive Write Overload Protection prevents this scenario. It constantly monitors the current state of the write queue and uses a carefully tuned algorithm to allow just enough queueing to maximize throughput on the available hardware while keeping latencies under control and unnecessary rejections to a minimum.
Write overload protection was added in Vault Enterprise 1.17 as a beta feature which is disabled by default.
To enable the feature use the adaptive_overload_protection configuration
stanza.
Metrics
Operators may wish to monitor metrics related to the write overload protection
controller. The most useful of these is the reject_fraction which represents
the controller's current estimate for the fraction of write requests that need
to be rejected to maintain optimal throughput and stability.
See the wal.write_controller.reject_fraction metrics reference.
Client handling of overloads
When Vault has reached capacity, new requests will be immediately rejected with
a retryable 503 - Service Unavailable. See Vault Server Temporarily
Overloaded
for additional considerations around handling this error correctly.